Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimals experience joy. Scientists want to measure it
Scientists have long focused on quantifying fear and other negative emotions in animals. Now they’re trying to measure positive feelings — and it’s a challenge.
By Amber Dance -
 Life
LifeThere’s life beneath the snow, but it’s at risk of melting away
An array of animals and plants survive winter in the subnivium, nature’s igloo. But climate change is threatening this hidden seasonal ecosystem.
-
 Plants
Plants'In Botanical Time' explores the ways Earth’s oldest plants cheat death
Author Christopher Woods unpacks the science behind ancient plants’ longevity in a new book.
By Jude Coleman - Animals
This tool-using cow defies expectations for bovine braininess
Veronika the cow uses a brush as a tool to scratch herself, revealing rare problem-solving skills and expanding what we know of tool use in animals.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis fish may play a hole in its head like a drum
The rockhead poacher is a little fish with a big pit in its head. The divot may be like a drum, making sound that rises above a chaotic, nearshore din.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsAnimal personalities can play a big role in saving species
From bold foxes to gregarious birds, animals’ personalities are increasingly being seen as crucial to conservation efforts.
-
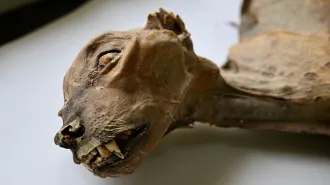 Animals
AnimalsHow cheetah mummies could help bring the species back to Arabia
Arabian cheetah mummies' DNA reveals that the long-lost population could be closely replaced by a cheetah population in northwestern Africa.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis dino’s fossil claw suggests it snatched eggs, not insects
A 67-million-year-old claw fossil reveals a new dinosaur species that may have used its hand spikes to snatch and pierce eggs.
-
 Plants
PlantsPlants packed close enough to touch are more resilient to stress
Signals transmitted via leaves can warn neighboring plants of stressful events, making the group collectively more resilient than plants in isolation.
-
 Physics
PhysicsQueen bumblebees are poor foragers thanks to sparse tongue hair
The density of fine hairs on bumblebees’ tongues determines how much nectar they can collect — and workers put queen bees to shame.
-
 Plants
PlantsIn a new kind of plant trickery, this yam fools birds with fake berries
Black-bulb yam’s mimicry tricks birds into spreading its berrylike clones. The plant's novel strategy helps it spread without seeds or sexual reproduction.
- Animals
Among chimpanzees, thrill-seeking peaks in toddlerhood
In humans, teens do the most dangerous things. In chimpanzees, that honor goes to toddlers. The difference may lie in caregiver supervision.
By Sujata Gupta