All Stories
-
 Climate
ClimateMaximum size for Arctic sea ice hits a new low
Warm temperatures helped drop the Arctic sea ice maximum to the smallest size on record.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyJapan’s new X-ray space telescope has gone silent
Japan’s newest orbiting X-ray telescope, ASTRO-H, has gone silent and might have broken into several pieces, the Japanese space agency reports.
-
 Health & Medicine
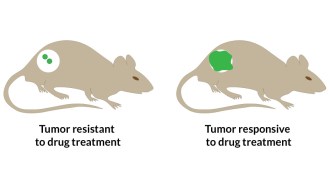
Health & MedicineCancer killers send signal of success
Newly designed nanoparticles deliver anticancer drugs and updates on tumor death.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy some male hyenas leave and others are content to stay home
Having access to enough females, and a mom to help, can keep a male hyena from leaving his clan.
-
 Earth
EarthBeware of rockfalls in warm weather
Cracks in cliff faces grow and shrink as temperatures warm and cool, new research shows.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySee life in a cubic foot, visit Roman artifacts, and more to do
New and upcoming exhibits celebrate biodiversity, birds’ dinosaur origins, opulence in ancient Rome, and more.
-

-
 Microbes
MicrobesDiverse yeasts make their home on coffee and cacao beans
Yeasts in coffee and cacao are shaped by geography and human migration, genetic analysis finds.
-
 Tech
TechA storm of tweets followed Superstorm Sandy’s path
When storms hit, people hunker down and tweet. Their social media activity tracks natural disasters and their damage, a new study shows.
-
 Climate
ClimateOrganic molecules help fatten cloud-making water droplets
Cloud-forming water droplets can grow larger thanks to organic molecules on the exterior of the drop, new research suggests.
-
 Genetics
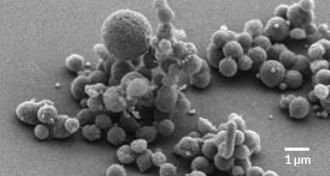
GeneticsScientists build minimum-genome bacterium
Minimal genome organism reveals how much scientists don’t know about biology.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsZika may have flown to Brazil in 2013
The brand of Zika currently floating around the Americas traces its origins to Asia and may have arrived in Brazil by air as early as 2013.