Uncategorized
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossil autopsy claims Lucy fell from tree
A contested study suggests a famous fossil ancestor plunged to her death.
By Bruce Bower -
-
 Physics
PhysicsBacteria-sized molecules created in lab
Cesium atoms with high-energy electrons pair up to form giant molecules.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSpacecraft reveal diversity in solar system’s landscapes
The latest generation of interplanetary spacecraft have revealed diverse landscapes on planets, asteroids and comets throughout the solar system.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceVenus once possibly habitable, study suggests
Venus might have once been habitable and home to a shallow ocean.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClean inside those bagpipes — and trumpets and clarinets
Bagpipes’ moist interiors may be the perfect breeding ground for yeasts and molds.
By Meghan Rosen -
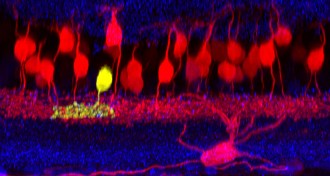
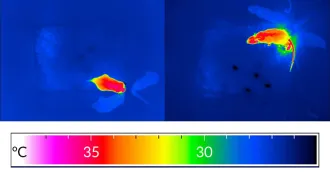 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCool nerve cells help mice beat heat
A new study pinpoints fever-busting cells in mice’s brains.
-
 Earth
EarthWave-thumping ‘weather bomb’ storms send elusive S waves through Earth
A rare type of deep-Earth tremor called an S wave generated by a rapidly strengthening storm could help scientists map the planet’s mantle and core.
-
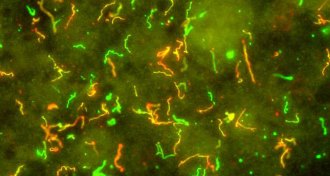 Life
LifeLyme bacteria swap ‘catch bonds’ to navigate blood vessels
Lyme bacteria use same tricks as white blood cells to navigate blood stream.
-
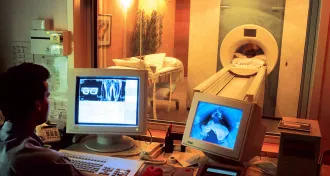 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceComputers refine epilepsy treatment
Surgeons harnessed computers in 1966 to pinpoint source of epilepsy in the brain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThank (or blame) your genes for ability to handle java jolt
A gene involved in caffeine processing may control coffee consumption.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWarm-up benefit could explain morning birdsong
Even birds sing better after vocal warm-up, and an evolutionary arms race among rivals might have led to the intensity of the dawn chorus.
By Susan Milius