Uncategorized
-
 Animals
Animals‘Silent Sparks’ illuminates fascinating world of fireflies
In a new book, a firefly researcher explores why scientists and kids alike are captivated by lightning bugs.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthA third of the population can’t see the Milky Way at night
Light pollution conceals the Milky Way’s star-spangled core from more than a third of Earth’s population, a global atlas of artificial sky luminance reveals.
-
 Plants
PlantsScary tomato appears to bleed
A new species of Australian bush tomato bleeds when injured and turns bony in old age.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyKids’ anxieties, depression need attention
Psychological troubles in childhood are no longer considered a part of normal development.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateVolcanic rocks help turn carbon emissions to stone — and fast
A pilot program in Iceland that injected carbon dioxide into basaltic lava rocks turned more than 95 percent of the greenhouse gas into stone within two years.
-
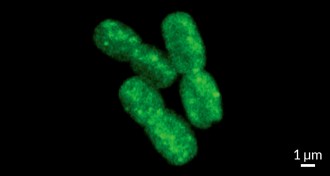 Ecosystems
EcosystemsOcean plankton held hostage by pirate viruses
The most abundant photosynthesizers on Earth stop storing carbon when they catch a virus.
By Susan Milius -
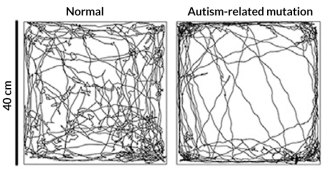 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAbnormal sense of touch may play role in autism
Autism-related genes are important for touch perception, a sense that may help the brain develop normally, a study of mice suggests.
-
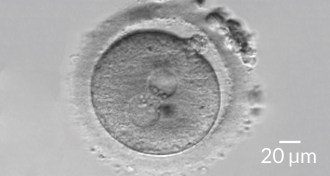 Life
LifeRefined ‘three-parent-baby’ procedure improves chances for healthy infant
Improved technique could reduce risk of passing on faulty mitochondria.
-
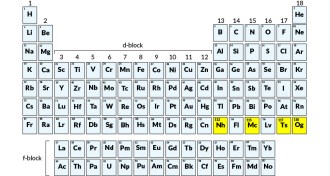 Chemistry
ChemistryFour newest elements on periodic table get names
Four elements officially recognized in December, highlighted in yellow, now have names that honor Japan, Moscow, Tennessee and physicist Yuri Oganessian.
-
 Life
LifeObesity’s weight gain message starts in gut
Acetate made by gut microbes stimulates weight gain, research in rodents suggests.
-
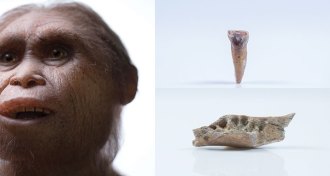 Anthropology
AnthropologyHobbit history gets new preface
Jaw, tooth fossils put new spin on evolution of Homo floresiensis.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeBy leaking light, squid hides in plain sight
Glass squid camouflage their eyes with wonderfully inefficient bioluminescence.
By Susan Milius