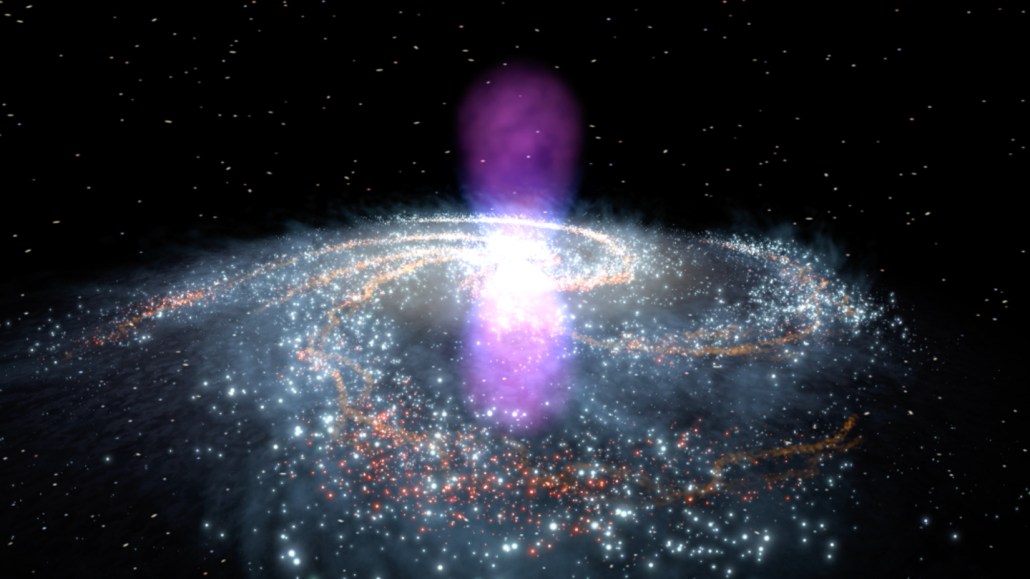
Two enormous bubbles of gas (blue and purple in this illustration) extend from the center of the Milky Way. Scientists think they’ve seen positrons, the antimatter counterparts to electrons, that came from the event that may have blown these Fermi bubbles many millennia ago.
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center