A Greek skull may belong to the oldest human found outside of Africa
Homo sapiens may have reached southeastern Europe as early as 210,000 years ago
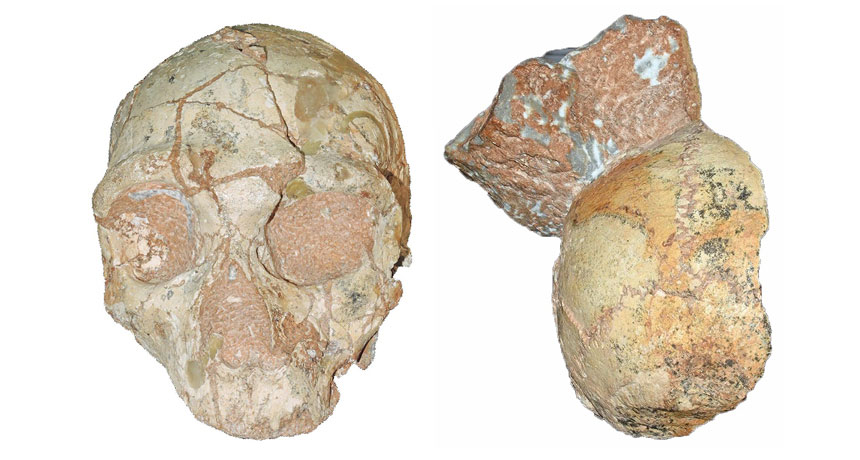
GREEK ENTRY Two partial skulls from a Greek cave, one identified as a Neandertal (left) and one as a Homo sapiens (right), point to a human presence in southeastern Europe more than 200,000 years ago followed by Neandertals replacing them at least 170,000 years ago.
K. Harvati/Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen
A skull found in a cliffside cave on Greece’s southern coast in 1978 represents the oldest Homo sapiens fossil outside Africa, scientists say.
That skull, from an individual who lived at least 210,000 years ago, was encased in rock that also held a Neandertal skull dating to at least 170,000 years ago, contends a team led by paleoanthropologist Katerina Harvati of the University of Tübingen in Germany.
If these findings, reported online July 10 in Nature, hold up, the ancient Greek H. sapiens skull is more than 160,000 years older than the next oldest European H. sapiens fossils (SN Online: 11/2/11). It’s also older than a proposed H. sapiens jaw found at Israel’s Misliya Cave that dates to between around 177,000 and 194,000 years ago (SN: 2/17/18, p. 6).
“Multiple Homo sapiens populations dispersed out of Africa starting much earlier, and reaching much farther into Europe, than previously thought,” Harvati said at a July 8 news conference. African H. sapiens originated roughly 300,000 years ago (SN: 7/8/17, p. 6).
A small group of humans may have reached what’s now Greece more than 200,000 years ago, she suggested. Neandertals who settled in southeastern Europe not long after that may have replaced those first H. sapiens. Then humans arriving in Mediterranean Europe tens of thousands of years later would eventually have replaced resident Neandertals, who died out around 40,000 years ago (SN Online: 6/26/19).
But Harvati’s group can’t exclude the possibility that H. sapiens and Neandertals simultaneously inhabited southeastern Europe more than 200,000 years ago and sometimes interbred. A 2017 analysis of ancient and modern DNA concluded that humans likely mated with European Neandertals at that time.
The two skulls were held in a small section of wall that had washed into Greece’s Apidima Cave from higher cliff sediment and then solidified roughly 150,000 years ago. Since one skull is older than the other, each must originally have been deposited in different sediment layers before ending up about 30 centimeters apart on the cave wall, the researchers say.
Two in one
To compare the sizes and shapes of two ancient Greek skulls, investigators superimposed a digital reconstruction of the face and partial braincase of a Neandertal (with its recovered pieces shown in different colors) over the back of a Homo sapiens braincase (shown in yellow). The results support the argument that the skulls do not come from the same species, the researchers say.
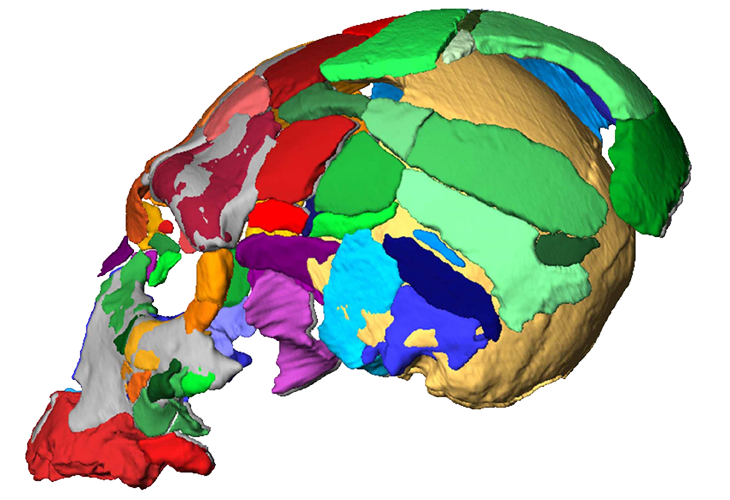
Earlier studies indicated that one Apidima skull, which retains the face and much of the braincase, was a Neandertal that lived at least 160,000 years ago. But fossilization and sediment pressures had distorted the skull’s shape. Based on four 3-D digital reconstructions of the specimen, Harvati’s team concluded that its heavy brow ridges, sloping face and other features resembled Neandertal skulls more than ancient and modern human skulls. An analysis of the decay rate of radioactive forms of uranium in skull bone fragments produced an age estimate of at least 170,000 years.
A second Apidima fossil, also dated using uranium analyses, consists of the back of a slightly distorted braincase. Its rounded shape in a digital reconstruction characterizes H. sapiens, not Neandertals, the researchers say. A bunlike bulge often protrudes from the back of Neandertals’ skulls.
But without any facial remains to confirm the species identity of the partial braincase, “it is still possible that both Apidima skulls are Neandertals,” says paleoanthropologist Israel Hershkovitz of Tel Aviv University. Hershkovitz led the team that discovered the Misliya jaw and assigned it to H. sapiens.
Harvati and her colleagues will try to extract DNA and species-distinguishing proteins (SN: 6/8/19, p. 6) from the Greek skulls to determine their evolutionary identities and to look for signs of interbreeding between humans and Neandertals.
The find does little to resolve competing explanations of how ancient humans made their way out of Africa. Harvati’s suggestion that humans trekked from Africa to Eurasia several times starting more than 200,000 years ago is plausible, says paleoanthropologist Eric Delson of City University of New York’s Lehman College in an accompanying commentary. And the idea that some H. sapiens newcomers gave way to Neandertals probably also applied to humans who reached Misliya Cave and nearby Middle Eastern sites as late as around 90,000 years ago, before Neandertals occupied the area by 60,000 years ago, Delson says.
Hershkovitz disagrees. Ancient humans and Neandertals lived side-by-side in the Middle East for 100,000 years or more and occasionally interbred, he contends. Misliya Cave sediment bearing stone tools dates to as early as 274,000 years ago, Hershkovitz says. Since only H. sapiens remains have been found in the Israeli cave, ancient humans probably made those stone artifacts and could have been forerunners of Greek H. sapiens.