Sacrificed dog remains feed tales of Bronze Age ‘wolf-men’ warriors
Find is first archaeological evidence of coming-of-age rites described in ancient myths, researchers claim
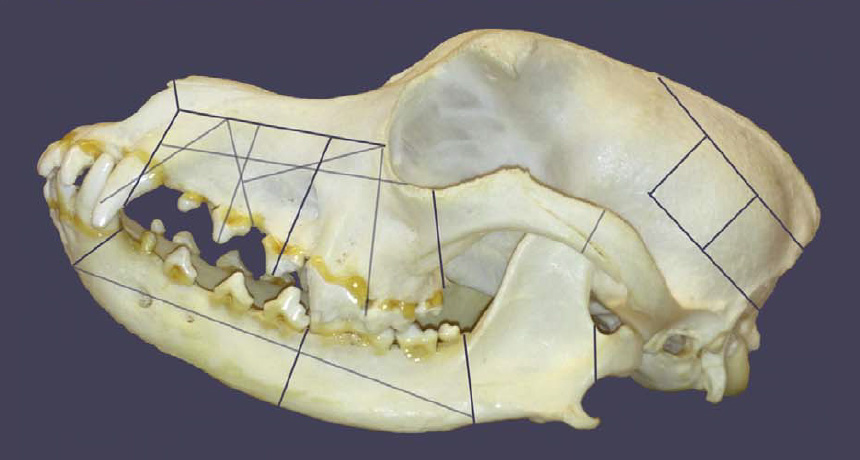
SLICE RITES Nearly 4,000 years ago, at a site in what’s now Russia, teenage boys ate dogs or wolves to join war bands, a contested report says. Dogs’ heads were commonly chopped in pieces designated by lines on this skull.
D. Anthony and D. Brown/Journal of Anthropological Archaeology 2017