Health & Medicine
-
 Life
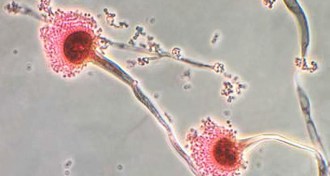
LifeWhen a fungus invades the lungs, immune cells can tell it to self-destruct
Immune system resists fungal infection by directing spores to their death.
-
 Neuroscience
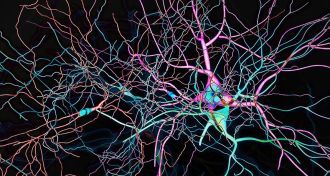
NeuroscienceBrain chemical lost in Parkinson’s may contribute to its own demise
A dangerous form of the chemical messenger dopamine causes cellular mayhem in the very nerve cells that make it.
-
 Health & Medicine
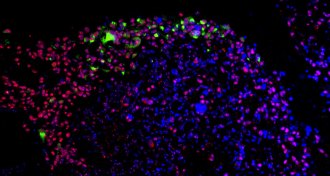
Health & MedicineZika could one day help combat deadly brain cancer
The Zika virus targets cells that cause glioblastoma, an aggressive form of brain cancer, studies in human cells and mice show.
-
 Health & Medicine
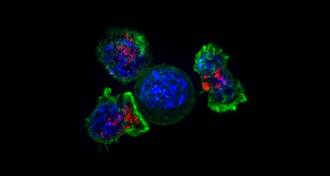
Health & MedicineFDA approves gene therapy to treat a rare cancer
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Kymriah to treat a rare cancer. It’s the first-ever gene therapy approved in the United States.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMuscle pain in people on statins may have a genetic link
Many people stop taking cholesterol drugs because of aches, but it has been unclear if the drugs are at fault.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow gut bacteria may affect anxiety
Microbes may tamper with the production of tiny molecules in brain regions that help control anxiety.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSeeing one picture at a time helps kids learn words from books
A small study found that children were better able to pick up vocabulary from books that show only one picture at a time.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth control research is moving beyond the pill
After decades of research, reproductive biologists are on the verge of developing new birth control options that stop sperm from maturing or save a woman's eggs for later.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new tool could one day improve Lyme disease diagnosis
There soon could be a way to differentiate between Lyme disease and a similar tick-associated illness.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineProtect little ones’ eyes from the sun during the eclipse
Pay attention to eye safety for kids during the solar eclipse.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing creates virus-free piglets
Pigs engineered to lack infectious viruses may one day produce transplant organs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore U.S. adults are drinking, and more heavily
Heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders have risen in the United States, at a cost to society’s health.