Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWeekend warriors put up a fight against death
Weekend warriors shove all their weekly activity into just one or two days, and it’s still enough to reduce mortality risk.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyLong-lasting mental health isn’t normal
Those who stay mentally healthy from childhood to middle age are exceptions to the rule.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLittle jet-setters get jet lag too
Help young children fight jet lag with a few simple steps.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarette smoking linked to heart disease risk
Two indicators of heart disease risk were elevated for users of e-cigarettes in small-scale study.
-
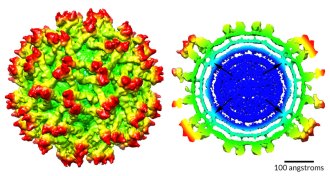 Life
LifeMap of Zika virus reveals how it shifts as it matures
A cryo-electron microscopy map of immature Zika virus offers a never-before-seen glimpse of remodeling of the virus’s protein and RNA core.
By Meghan Rosen -
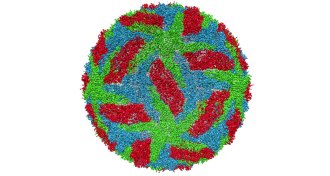 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRogue antibody linked to severe second dengue infections
Alternate antibody may indicate whether someone is susceptible to severe dengue disease.
-
 Life
LifeWhy salmonella doesn’t want you to poop out
Salmonella bacteria fight infection-driven losses in appetite to keep hosts just healthy enough for transmission.
-
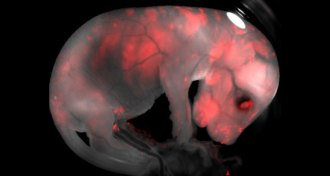 Life
LifeMouse cells grown in rats cure diabetes in mice
Mixing cells of two species produces pig and cattle embryos with some human cells.
-
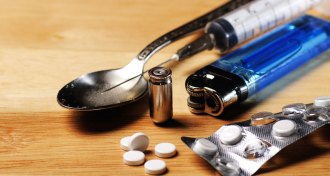 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, methadone made a rosy debut
Heralded as the “answer to heroin addiction,” methadone is still used to treat opiate addiction, despite risks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA ban on screens in bedrooms may save kids’ sleep
Screens are associated with worse sleep in kids, and not just because of their lights and noises.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyReal-life adventure tale details search for legendary city
"The Lost City of the Monkey God" recounts archaeological expedition to uncover truth behind Honduras’ “White City" myth.
By Erin Wayman -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCancer studies get mixed grades on redo tests
Replications of cancer studies fail to reproduce some results.