Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Tech
TechStretchy silicon sticker monitors your heartbeat
A new stretchy memory device looks like a temporary tattoo and works like a heart rate monitor.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyAs suicide rates rise, researchers separate thoughts from actions
Advances in suicide research and treatment may depend on separating thoughts from acts.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHow seeing ‘Star Wars’ satisfies your narcissistic tendencies
Participating in geek culture allows self-identified geeks to satisfy a narcissistic need for expert status, a new study hypothesizes.
-
 Health & Medicine
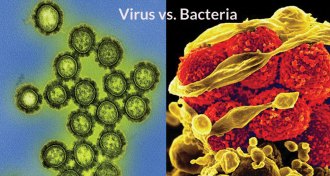
Health & MedicineGene behavior distinguishes viral from bacterial infections
Researchers have identified signatures of viral infection, a distinction that may help doctors tell whether bacteria or a virus is causing trouble.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyIn science, a lack of replication shouldn’t kill your reputation
The proof is science is when a study is replicated. When it’s not, do scientists suffer? A new study says researchers may overestimate the negative effects.
-
 Health & Medicine
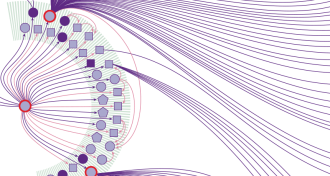
Health & MedicineAnatomy of the South Korean MERS outbreak
The Middle East respiratory syndrome virus, which infected 186 people in South Korea in 2015, quickly spread within and between hospitals via a handful of “superspreaders.”
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCow bites and spacecraft injuries enliven new medical diagnostic codes
The 10th edition of International Classification of Diseases went into effect in 2015, and it included some interesting additions.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThigh bone adds to mystery over 14,000-year-old Homo species
Controversial Chinese leg fossil may point to hybrid humans 14,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
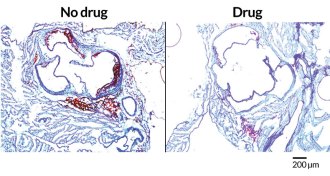
Health & MedicineTo treat the heart, start with the gut
Preventing gut bacteria from making certain chemical compounds reduced artery clogging in mice, researchers report.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyLinks between scrapie and MS less likely
Five decades later, scientists still puzzle over what causes multiple sclerosis.
-
 Life
LifeIn the body, cells move like flocks of birds or schools of fish
Cells move in groups similarly to flocks of birds and schools of fish
-
 Neuroscience
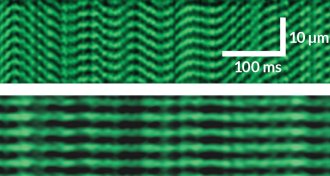
NeuroscienceMini microscope is a window into live muscle tissue
A tiny microscope offers unprecedented views of live human muscles.