Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSouth Americans may have traveled to Polynesia 800 years ago
DNA analyses suggest that Indigenous people from South America had a role in the early peopling of Polynesia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeBizarre caecilians may be the only amphibians with venomous bites
Microscope and chemical analyses suggest that, like snakes, caecilians have glands near their teeth that secrete venom.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA sparrow song remix took over North America with astonishing speed
A variation on the white-throated sparrow’s song spread 3,300 kilometers in just a few decades.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Life
LifeHere’s how flying snakes stay aloft
High-speed cameras show that paradise tree snakes keep from tumbling as they glide through the sky by undulating their bodies.
-
 Life
LifeFish eggs can hatch after being eaten and pooped out by ducks
In the lab, a few carp eggs survived and even hatched after being pooped out by ducks. The finding may help explain how fish reach isolated waterways.
-
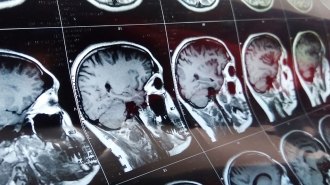 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStrokes and mental state changes hint at how COVID-19 harms the brain
In a group of people severely ill from the coronavirus, strokes, psychosis, depression and other brain-related changes come as complications.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins can learn from peers how to use shells as tools
While most foraging skills are picked up from mom, some bottlenose dolphins seem to look to their peers to learn how to trap prey in shells.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil discoveries suggest the earliest dinosaurs laid soft-shelled eggs
Finding soft-shelled dinosaur eggs in the fossil record for the first time has scientists rethinking how dinosaur eggs evolved.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Tech
TechBubble-blowing drones may one day aid artificial pollination
Drones are too clumsy to rub pollen on flowers and not damage them. But blowing pollen-laden bubbles may help the machines be better pollinators.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow to make a mouse smell a smell that doesn’t actually exist
The ability to create a perception might lead to a deeper understanding of how the brain makes sense of the world.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA from a 5,200-year-old Irish tomb hints at ancient royal incest
Ruling families in Ireland may have organized a big tomb project, and inbred, more than 5,000 years ago, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsBarn owlets share food with their younger siblings in exchange for grooming
Scientists weren’t sure why elder barn owlets would give away meals to their younger kin, a rare example of sibling cooperation in birds.
By Pratik Pawar