Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeLarge predators push coyotes and bobcats near people and to their demise
Coyotes and bobcats hide near people when wolves, cougars and other large predators are close-by, putting the smaller carnivores at a higher risk of dying at human hands.
By Freda Kreier -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA rare mutation helped one man stave off Alzheimer’s for decades
The brain of a Colombian man with an inherited form of Alzheimer’s may hint at ways to halt or slow the progression of the disease.
By Simon Makin -
 Animals
AnimalsThe Sonoran Desert toad can alter your mind — it’s not the only animal
Their psychedelic and other potentially mind-bending compounds didn't evolve to give people a trip.
-
 Life
LifeIn one lake deep under Antarctica’s ice, microbes feast on ancient carbon
Microorganisms living in a lake beneath the ice sheet in West Antarctica feed on ocean carbon that was deposited 6,000 years ago.
By Freda Kreier -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy some hammerhead sharks seem to ‘hold their breath’ during dives
Scalloped hammerhead sharks in Hawaii seem to limit the use of their gills during deep dives to prevent losing heat to their surroundings.
By Freda Kreier -
 Paleontology
Paleontology‘Thunder beast’ fossils show how some mammals might have gotten big
Rhinolike mammals called brontotheres repeatedly evolved into bigger and smaller species, a fossil analysis shows. The bigger ones won out over time.
By Elise Cutts -
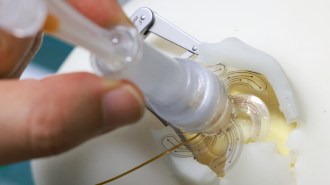 Tech
TechA flower-shaped soft robot could make brain monitoring less invasive
Once inserted in the skull, the device unfurls flexible sensors that can monitor the brain's electrical activity less invasively than current methods.
By Bob Hirshon -
 Life
LifeThe new human pangenome could help unveil the biology of everyone
The deciphered DNA includes never-before-explored parts of the genome and better represents the genetic diversity of all humans.
-
 Life
LifeAncient giant eruptions may have seeded nitrogen needed for life
A new study bolsters the idea that on the young Earth volcanic lightning may have provided some materials that made it possible for life to emerge.
By Bas den Hond -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnancy may hamper bats’ ability to ‘see’ in the dark
Tiny Kuhl’s pipistrelle bats make fewer calls when pregnant, which may make it more difficult to hunt prey, lab tests hint.
By Freda Kreier -
 Life
LifeSwarming locusts can deploy a chemical to avoid being cannibalized
Releasing a “don’t-eat-me” pheromone signals a locust has become a toxic treat. The finding could lead to new ways to control destructive swarms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA has approved the first-ever vaccine for RSV
GSK’s shot, for those 60 and over, can protect against severe respiratory syncytial virus. Other vaccines, including to protect newborns, are in the works.