News
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyNew JWST images suggest our understanding of the cosmos is flawed
JWST data don’t resolve a disagreement over how fast the universe is expanding, suggesting we might need strange new physics to fix the tension.
-
Antimatter falls like matter, upholding Einstein’s theory of gravity
In a first, scientists dropped antihydrogen atoms and measured how they fell.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA one-of-a-kind trilobite fossil hints at what and how these creatures ate
The preserved contents suggest the trilobite fed almost continuously and had a gut environment with an alkaline or neutral pH, researchers say.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsSeen Bigfoot or the Loch Ness Monster? Data suggest the odds are low
Floe Foxon is a data scientist by day. But in his free time, he applies his skills to astronomy, cryptology and sightings of mythical creatures.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how much coronavirus people infected with COVID-19 may exhale
Just breathing naturally can lead people with COVID-19 to emit dozens of copies of viral RNA a minute and that can persist for eight days, a study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese brainless jellyfish use their eyes and bundles of nerves to learn
No brain? No problem for Caribbean box jellyfish. Their seemingly simple nervous systems can learn to avoid obstacles on sight, a study suggests.
-
 Space
SpaceNASA’s OSIRIS-REx has returned bits of the asteroid Bennu to Earth
Asteroid dirt from Bennu could help reveal clues about the material that came together to make the solar system — and possibly where life comes from.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouth taping may be a trending sleep hack, but the science behind it is slim
Mouth taping is big on social media, but few studies have evaluated it. Some evidence suggests that sealing the lips shut may help people with sleep apnea.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyInterlocking logs may be evidence of the oldest known wooden structure
Roughly 480,000-year-old wooden find from Zambia suggests early hominids were more skilled at structuring their environments than scientists realized.
-
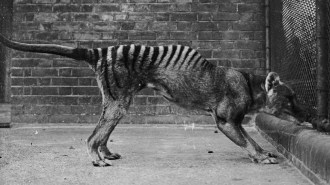 Animals
AnimalsFor the first time, researchers decoded the RNA of an extinct animal
The Tasmanian tiger, or thylacine, was hunted nearly to extinction. Now RNA extracted from a museum specimen reveals how its cells functioned.
-
 Earth
EarthTo form pink diamonds, build and destroy a supercontinent
The Argyle deposit in Australia formed about 1.3 billion years ago, a study shows, along a rift zone that sundered the supercontinent Nuna.
By Nikk Ogasa -
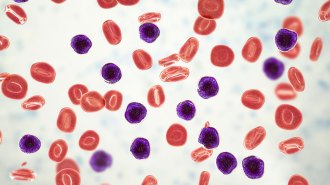 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA catalog of all human cells reveals a mathematical pattern
Smaller cells occur in larger numbers in the human body, and cells of different size classes contribute equally to our overall mass.