Uncategorized
-
 Animals
AnimalsPiggybacking tadpoles are epic food beggars
Tadpoles beg so frantically among mimic poison frogs that researchers check to see whether they’re just scamming.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeTyphoid toxin aids survival in mice
A DNA-damaging bacterial protein may prolong the lives of infected animals.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyKey sugar needed for life could have formed in space
Sugar that forms backbone of cell machinery can form on icy grains blasted by ultraviolet light from young stars.
-
 Life
Life‘Wild Ways’ showcases need for wildlife corridors
The TV documentary 'Wild Ways' shows how wildlife corridors bridge the gap between isolated populations of animals.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyPossible source of high-energy neutrino reported
Scientists may have found the cosmic birthplace of an ultra-high energy neutrino: a blazar 9 billion light years away.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLip-readers ‘hear’ silent words
Lipreading prompts activity in the brain’s listening area.
-
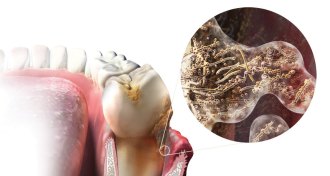 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGum disease opens up the body to a host of infections
Researchers are getting to the root of gum disease's implications for other diseases.
By Laura Beil -
 Climate
ClimateSea levels could rise twice as fast as previously predicted
Sea level rise from Antarctica’s melting ice could accelerate faster and sooner than previously thought.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThere’s far more to the galaxy than meets the eye
A new map of the galaxy as seen in submillimeter light reveals intricate details from nearby nebulas to the far-flung galactic center.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThis microbe makes a meal of plastic
A newly identified bacterium can break down plastic waste.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHippocampus makes maps of social space, too
The hippocampus is a multitalented mapmaker.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDome effect leaves Chinese megacities under thick haze
Airborne black carbon lowers an atmospheric boundary, trapping pollution around major cities and worsening air quality, researchers propose.