Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny glasses help reveal how praying mantises can see in 3-D
Newfound nerve cells in praying mantises help detect different views that each of the insects’ eyes sees, a mismatch that creates depth perception.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA Greek skull may belong to the oldest human found outside of Africa
Humans possibly reached southeastern Europe by 210,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineToddlers tend to opt for the last thing in a set, so craft your questions carefully
Two-year-olds demonstrate a verbal quirk that makes their answers less reliable.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient humans used the moon as a calendar in the sky
Whether the moon was a timekeeper for early humans, as first argued during the Apollo missions, is still up for debate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBreaking down the science behind some of your favorite summer activities
Inject some science into your summer.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA reveals the origins of the Philistines
A mysterious Biblical-era population may have fled Bronze Age calamities.
By Bruce Bower -
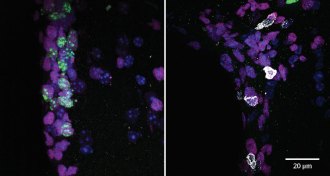 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRogue immune cells can infiltrate old brains
Killer T cells get into older brains where they may make mischief, a study in mice and postmortem human brain tissue finds.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyEast Asians may have been reshaping their skulls 12,000 years ago
An ancient skull-molding practice had a long history in northeastern Asia, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
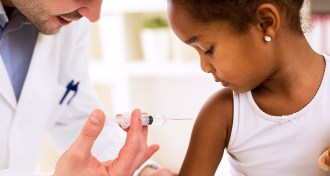 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCalifornia’s new vaccine rules kept more kindergartners up-to-date
Three statewide interventions improved the rates of kindergartners behind on required vaccinations in California, researchers report.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVision cells can pull double duty in the brain, detecting both color and shape
Neurons in a brain area that handles vision fire in response to more than one aspect of an object, countering earlier ideas, a study in monkeys finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn mice, a high-fat diet cuts a ‘brake’ used to control appetite
A fatty diet changes the behavior of key appetite-regulating cells in a mouse brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntioxidants may encourage the spread of lung cancer rather than prevent it
Antioxidants protect lung cancer cells from free radicals, but also spur metastasis, two new studies suggest.