Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAfrica’s first herders spread pastoralism by mating with foragers
DNA unveils long-ago hookups between early pastoralists and native hunter-gatherers in Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA fungus weaponized with a spider toxin can kill malaria mosquitoes
In controlled field experiments in Burkina Faso, a genetically engineered fungus reduced numbers of insecticide-resistant mosquitoes that can carry malaria.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryVaping the sweetener sucralose may produce toxic chemicals
Sucralose in e-liquids can break down, increasing toxic aldehydes in vapors and producing harmful organochlorines, including a potential carcinogen.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResurgence of measles is a tale as old as human history
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the recent global measles outbreak and the history of the spread of pathogens.
By Nancy Shute -
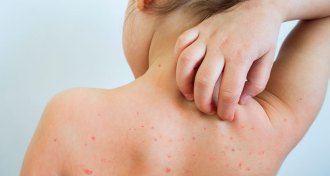 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne number can help explain why measles is so contagious
The basic reproduction number, or "R naught," of measles shows how contagious the disease is compared with other pathogens.
-
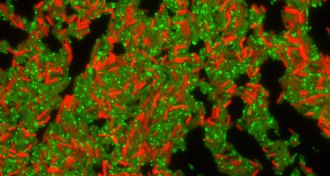 Life
LifeHow bacteria nearly killed by antibiotics can recover — and gain resistance
A pump protein can keep bacteria alive long enough for the microbes to develop antibiotic resistance.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBeing bilingual is great. But it may not boost some brain functions
A large study of U.S. bilingual children didn’t turn up obvious benefits in abilities to ignore distractions or switch quickly between tasks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFaulty cellular antennae may cause a heart valve disorder
Mitral valve prolapse might be caused by dysfunctional primary cilia meant to signal cells during development.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA cognitive neuroscientist warns that the U.S. justice system harms teen brains
The U.S. justice system holds adolescents to adult standards, and puts young people in situations that harm their development, a researcher argues.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHow the battle against measles varies around the world
Measles is a global health threat. Snapshots of several countries show how stopping its spread depends on local conditions and beliefs.
By Sujata Gupta -
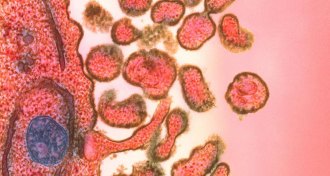 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles erases the immune system’s memory
The measles virus can usher in other infections for months, or even years.
-
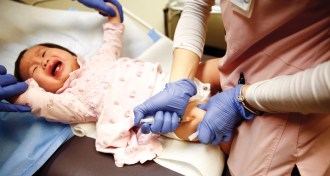 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFinding common ground can reduce parents’ hesitation about vaccines
Physicians are examining whether discussing shared health goals can bring vaccine-hesitant parents on board.