Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
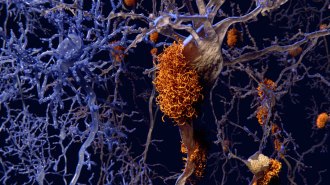
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s may scramble metabolism’s connection to sleep
Mice designed to have brain changes that mimic Alzheimer’s disease have altered reactions to blood sugar changes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhite bellbirds have the loudest known mating call of any bird
White bellbirds have the loudest mating call, according to scientists who compared the songs of bellbirds and screaming pihas in the Brazilian Amazon.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeA peek inside a turtle embryo wins the Nikon Small World photography contest
The annual competition highlights the wonders to be found when scientists and photographers zoom in on the world around us.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew books explore why dogs and humans have such a special bond
‘Dog Is Love’ and ‘Our Dogs, Ourselves’ delve into the complicated, sometimes contradictory relationship that we have with our canine companions.
-
 Health & Medicine
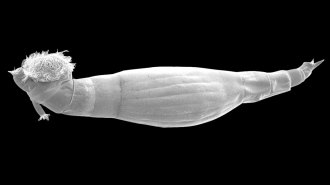
Health & MedicineThese tiny aquatic animals secrete a compound that may help fight snail fever
A newly identified molecule from rotifers paralyzes the larvae of worms that cause schistosomiasis, which affects over 200 million people worldwide.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
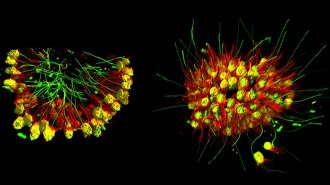
LifeAcrobatic choanoflagellates could help explain how multicellularity evolved
A newfound single-celled microbe species forms groups of multiple individual organisms that change shape in response to light.
-
 Paleontology
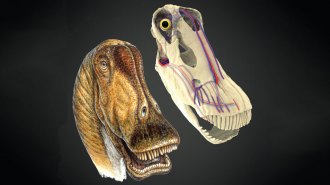
PaleontologyBig dinosaurs kept cool thanks to blood vessel clusters in their heads
Giant dinosaurs evolved several strategies for cooling their blood and avoiding heatstroke.
-
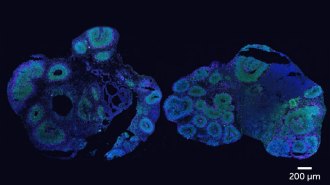 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOrganoids offer clues to how brains are made in humans and chimpanzees
Three-dimensional clumps of brain cells offer clues about how brains get made in humans and chimpanzees.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA precision drug for prostate cancer may slow the disease’s spread
The drug olaparib could be used to treat men with certain genetic mutations and severe types of prostate cancer, a clinical trial finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Animals
AnimalsHumpback whales use their flippers and bubble ‘nets’ to catch fish
A study reveals new details of how humpback whales hunt using their flippers and a whirl of bubbles to capture fish.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeExtreme snowfall kept most plants and animals in one Arctic ecosystem from reproducing
A very snowy winter in 2018 left parts of Greenland covered well into the summer, causing an ecosystem-wide reproductive collapse in one area.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient European households combined the rich and poor
Homes combined “haves” and “have-nots” in a male-run system, suggests a study that challenges traditional views of ancient social stratification.
By Bruce Bower