Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsStanley Qi gives CRISPR a makeover to redefine genetic engineering
By adapting CRISPR/Cas9, Stanley Qi has given genetic engineers a plethora of new tools.
-
 Climate
ClimateMalin Pinsky seeks to explain how climate change alters ocean life
As global temperatures rise, Malin Pinsky’s research attempts to understand how marine ecosystems are changing and why.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDog behaviors like aggression and fearfulness are linked to breed genetics
A study looking at how 101 dog breeds behave finds a strong association between genetics and 14 personality traits.
-
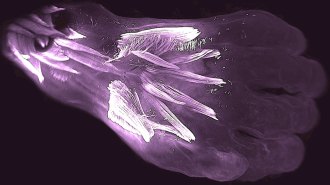 Humans
HumansHuman embryos have extra hand muscles found in lizards but not most adults
In developing human embryos, muscles are made, then lost, in a pattern that mirrors the appearance of the structures during evolution.
-
 Humans
HumansPersonalized diets may be the future of nutrition. But the science isn’t all there yet
How a person responds to food depends on more than the food itself. But what exactly is still a confusing mix of genes, microbes and other factors.
-
 Space
Space‘Imagined Life’ envisions the odd critters of other planets
The authors of ‘Imagined Life’ rely on science to sketch out what kind of organisms might exist on exoplanets.
By Sid Perkins -
 Life
LifeConnecting our dwindling natural habitats could help preserve plant diversity
As pristine habitats shrink worldwide, a massive, 18-year experiment suggests that linking up what's left with natural corridors could help ecosystems retain plant diversity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA mouse’s metabolism may follow circadian rhythms set by gut bacteria
While animals’ circadian clocks control functions from sleep to hormone release, gut bacteria dictate when mice’s small intestines take up fat.
-
 Life
LifeLosing genes may have helped whales’ ancestors adapt to life under the sea
Jettisoning genes tied to saliva and the lungs, among others, could have smoothed ancient cetaceans’ land-to-water transition 50 million years ago.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow climate change is already altering oceans and ice, and what’s to come
A new IPCC report gives the lowdown on how climate change is already wreaking havoc on Earth’s oceans and frozen regions, and how much worse things could get.
-
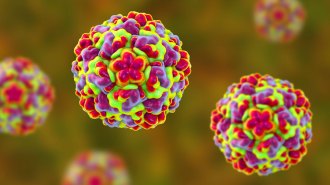 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDisabling one protein might one day lead to a cure for the common cold
Scientists have identified a protein in humans that some viruses, including those that cause colds, need to spread.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeCats may have ‘attachment styles’ that mirror people’s
In a new study, 65 percent of felines formed secure attachments with their owners. Like people, other cats were ambivalent or avoidant.
By Sofie Bates