Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Materials Science
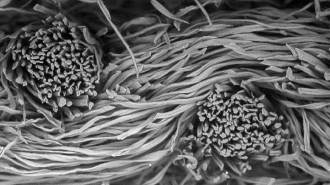
Materials ScienceMicroscopic images reveal the science and beauty of face masks
Important insights into the particle-filtering properties of different fabrics also offer a sense of the unseen, textured world of face masks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine4 takeaways from the WHO’s report on the origins of the coronavirus
The leading hypothesis is that the coronavirus spread to people from bats via a yet-to-be-identified animal, but no animals have tested positive so far.
-
 Health & Medicine
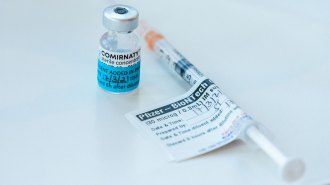
Health & MedicinePfizer says its COVID-19 vaccine has 100 percent efficacy in young people
Vaccinated 12- to 15-year-olds developed higher levels of coronavirus antibodies compared with vaccinated 16- to 25-year-olds from a previous trial.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFrog skin cells turned themselves into living machines
The “xenobots” can swim, navigate tubes, move particles into piles and even heal themselves after injury, a new study reports.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStone Age culture bloomed inland, not just along Africa’s coasts
Homo sapiens living more than 600 kilometers from the coast around 105,000 years ago collected crystals that may have had ritual meaning.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineModerna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines may block infection as well as disease
The mRNA vaccines are about 90 percent effective at blocking coronavirus infection, which could lead to reduced transmission, real-world data suggest.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s why humans chose particular groups of stars as constellations
Distances between stars, their brightnesses and patterns of human eye movement explain why particular sets of stars tend to be grouped together.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyParents in Western countries report the highest levels of burnout
The first survey comparing parental exhaustion across 42 countries links it to a culture of self-reliance.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
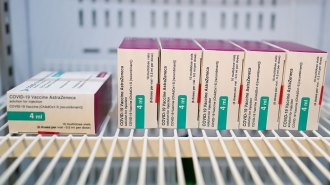
Health & MedicineAstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine holds up in an updated analysis of trial data
The redo dropped the overall efficacy of AstraZeneca’s vaccine from 79 percent to 76 percent. But a slight fluctuation is not unexpected, experts say.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow using sheepskin for legal papers may have prevented fraud
Removing fat is key to turning animal skin into parchment. With sheepskin, the process creates a writing surface easily marred by scratched-out words.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDim lighting may raise the risk of a West Nile virus exposure
Dimly lit nights increased risk of West Nile virus exposure in chickens. Artificial light proved a better predictor of risk than population or paving.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what makes 4 promising COVID-19 vaccines unique — and potentially useful
More vaccines still in the works are exploring a variety of approaches, including pills and electrical zaps.