Animal sex lives exposed in ‘Nature’s Nether Regions’
What the sex lives of bugs, birds, and beasts tell us about evolution, biodiversity, and ourselves.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

What the sex lives of bugs, birds, and beasts tell us about evolution, biodiversity, and ourselves.

NASA’s newly revealed Z-2 space suit is the second mock-up of a suit that NASA hopes will eventually protect explorers walking on Mars or drilling into an asteroid.

The first Thorne-Żytkow Object, a strange pair of stars where one engulfs the other, has been discovered.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
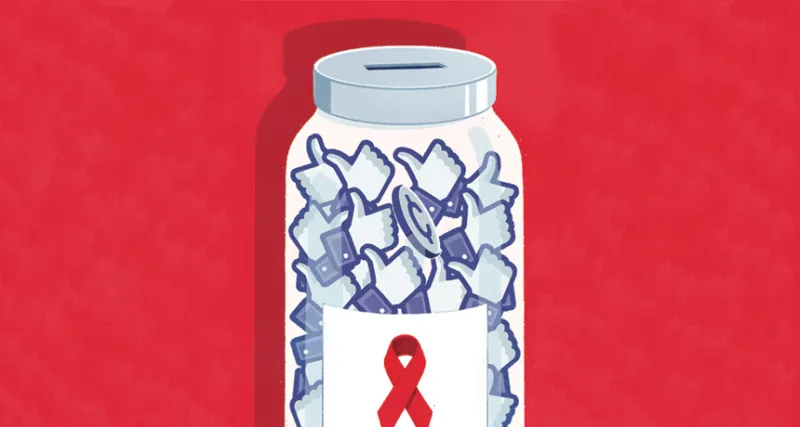

Online awareness campaigns can make people feel they’ve contributed to a good cause, but social scientists say the tangible benefits of such efforts may be small.

A male fairy wrasse gets feisty when he can see a rival’s colorful fluorescent patches.

Engineered bacterium singlehandedly dismantles tough switchgrass molecules, making sugars that it ferments to make ethanol.

Genes of the long-lived blind mole-rat help explain how the animal evades cancer and why it lost vision.

Kepler-10c is a rocky exoplanet 17 times as massive as Earth, and astronomers are puzzled as to how it formed.

Drooping against bark during a heat wave could save koalas from overheating.

Fruit flies deprived of the element bromine can’t make normal connective tissue that supports cells and either don’t hatch or die as larvae.
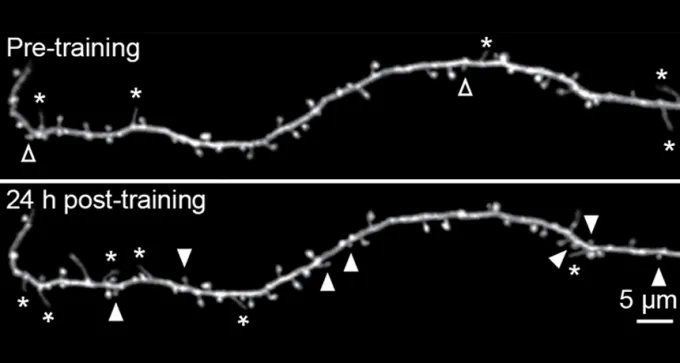
Mice show signs of stronger neuron connections when allowed to sleep after learning a trick.

A new chemical measurement of rocks from Earth and from the moon supports the giant impact hypothesis, which explains how the moon formed billions of years ago.

New images reveal a jet of particles shooting out of a collision among four galaxy clusters.

The first 3-D pterosaur eggs, which were found in China, suggest that the flying reptiles laid eggs together.

A simple invisibility cloak relies on hazy environments to mask objects.

When they turn down a good meal for a lesser one, rodents regret their choice, a study suggests.

Two new telescope concepts compete for NASA’s approval, in hopes of taking the first picture of a life-bearing exoplanet.
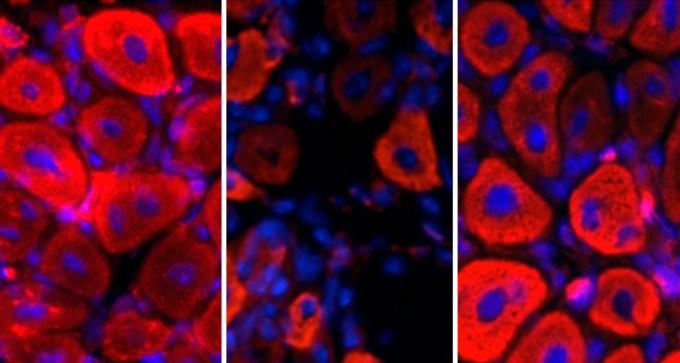
The naturally produced hormone oxytocin, well known for its role in social bonding, may help heal injured muscles in the elderly.

Winter road salt treatments boost sodium in roadside plants and alter development for monarch butterflies.
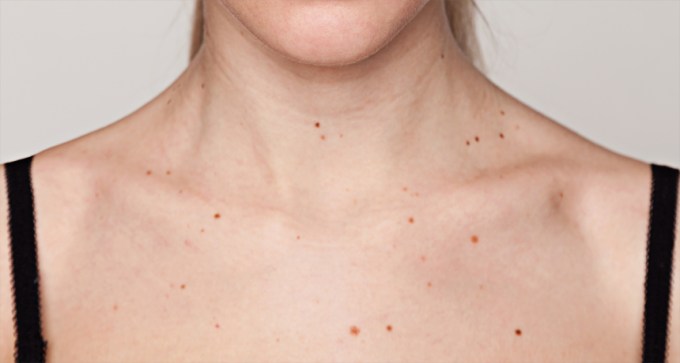
Women who have many moles also have increased disease risk, which may reflect higher estrogen levels.

New estimates of chimpanzee mutation rates suggest humans and chimps last shared a common ancestor 13 million years ago.
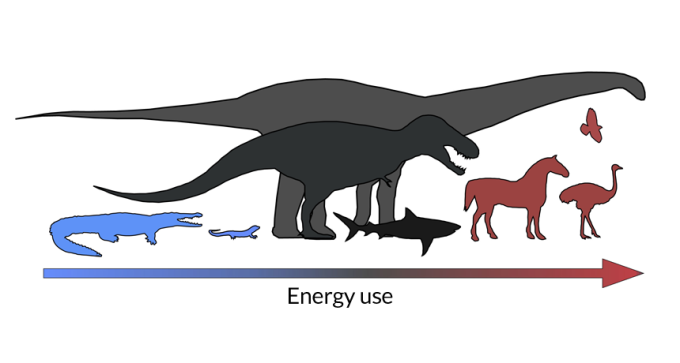
Tyrannosaurus rex and other dinosaurs straddled line between cold- and warm-blood, a new analysis finds.
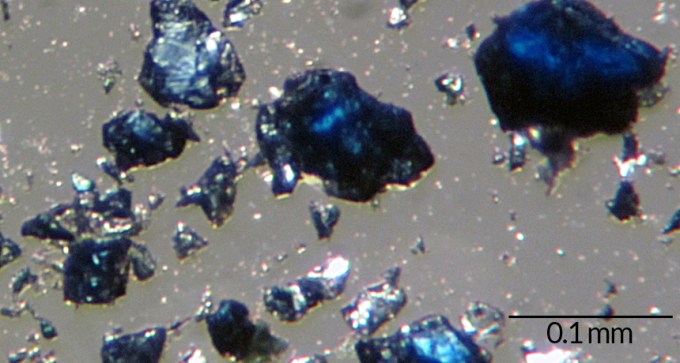
Ocean’s worth of water trapped in Earth’s mantle, lab experiments and seismic data suggest.

A room-temperature polariton laser, which requires little electricity, could improve electronics and medical devices.

Acute lung impacts of e-cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes are nearly identical, new study finds.
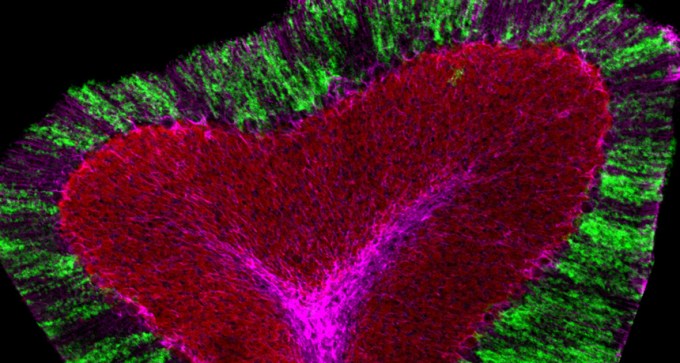
Norepinephrine, a stress hormone, wakes up cells called astroglia, possibly shifting brain into vigilant state.
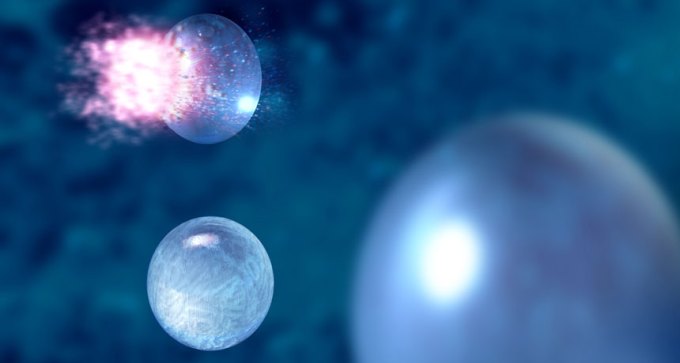
Weird supercooled water well below its freezing point viewed with ultrafast laser.

Excerpt from the July 11, 1964, issue of Science News Letter.

Ant lions are ferocious predators, but some of them don’t have a mouth. At least not in the usual sense.

At the lowest registers of the human voice, a creaky, popping sound known as vocal fry emerges.
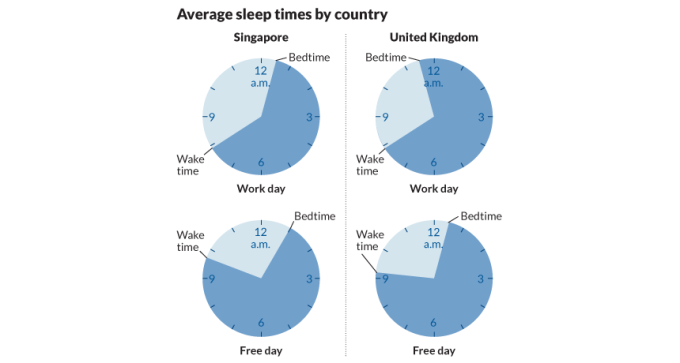
Sleep schedules vary from country to country, with social demands like work and study providing the primary incentives to stay up.

Authors Nancy Forbes and Basil Mahon show how two men’s work came together to change physics.

Improve your backyard birding using facial recognition software.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.