Chemistry
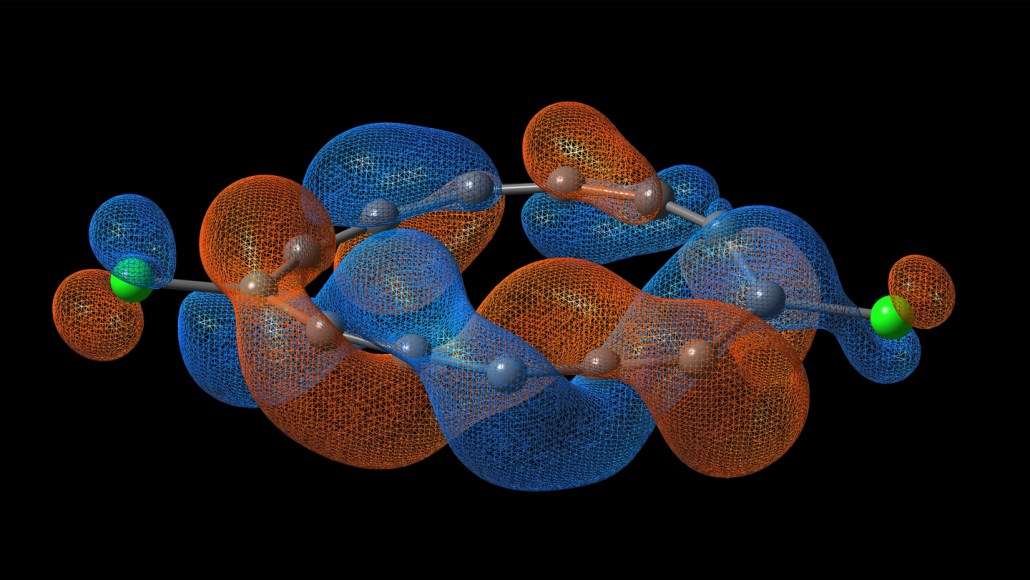
This molecule puts a new twist on the Möbius strip
A molecule made of carbon and chlorine is half as twisty as the paper loops common in math classes.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

A molecule made of carbon and chlorine is half as twisty as the paper loops common in math classes.
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.

When infected by a fungal disease, ant pupae actively emit a chemical cue that prompts workers to get rid of them for the good of the colony.
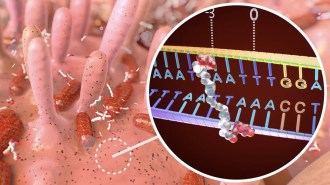
A closeup look at colibactin’s structure reveals chemical motifs that guide its mutation-wreaking “warheads” to specific stretches of DNA.

Simple chemistry could give the reindeer his famously bright snout. But physics would make it look different colors from the ground.
An AI tool trained on chemical signatures from corpse-eating insects may help determine time and place of death for victims of violent crimes.
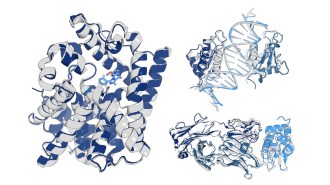
The open-source AI model improves transparency in predicting how proteins interact with other molecules, which could speed up drug discovery.

Pricey civet coffee gets its cred from its journey through the mammal’s gut, which changes the content of fat, protein, fatty acids — and even caffeine.

Richard Robson, Susumu Kitagawa and Omar Yaghi developed metal-organic frameworks, structures that can collect water from air, capture CO₂ and more.

Grape plant bacteria might help mitigate smoke taint in wine by breaking down chemicals that evoke an ashy taste.

Building blocks of life have been found on this moon of Saturn. They may come from chemical reactions beyond Enceladus’ possible life-supporting ocean.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber?
Become one now.