Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
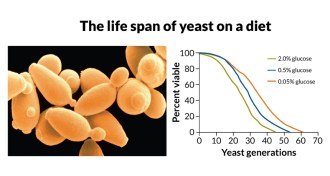
LifeCutting calories lets yeast live longer
A new study confirms yeast live longer on fewer calories.
-
 Life
LifeA downy killer wages chemical warfare
The common fungus Beauveria bassiana makes white downy corpses of its victims.
By Beth Mole -
 Genetics
GeneticsMutation-disease link masked in zebrafish
Zebrafish study shows organisms can work around DNA mutations.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSwimming bacteria remove resistance to flow
The collective motion of swimming bacteria can virtually eliminate a water-based solution’s resistance to flow.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsChildren’s classic ‘Watership Down’ is based on real science
The novel ‘Watership Down’ is the tale of a bunch of anthropomorphized rabbits. Their language may be unreal, but the animals’ behavior was rooted in science.
-
 Plants
PlantsFlowers’ roles considered in ecosystems and economics
In ‘The Reason for Flowers’, a pollination ecologist chronicles the science and culture of blossoms from the dawn of humanity.
By Sid Perkins -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient comb jellies might have had skeletons
Soft and filmy today, comb jellies might once have had rigid skeletons.
By Susan Milius -
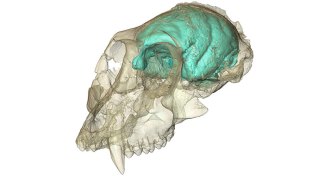 Anthropology
AnthropologyMonkey’s small brain shows surprising folds
An ancient monkey’s tiny brain developed folds, raising questions about primate evolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeWomen blush when ovulating, and it doesn’t matter a bit
Women don’t signal their fertility in obvious ways like nonhuman primates. A new study shows that even skin flushes are too subtle to detect.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant pandas live in the slow lane
Giant pandas burn far less energy than similarly sized land mammals.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Climate
ClimateBumblebee territory shrinking under climate change
Climate change is shrinking bumblebee habitat as southern territories heat up and bumblebees hold their lines in the north.
By Beth Mole -
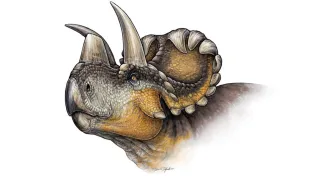 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow dinos like Triceratops got their horns
A new dino named Wendiceratops pinhornensis gives hints about how Triceratops and other relatives got their horns.