‘Eruption’ looks back at devastating Mount St. Helens blast
In Eruption, a science writer recounts the societal, economic and geologic forces that contributed to the Mount St. Helens disaster.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Colliding black holes send ripples through spacetime that can be detected here on Earth. What are these gravitational waves, and how did Advanced LIGO detect them?

In Eruption, a science writer recounts the societal, economic and geologic forces that contributed to the Mount St. Helens disaster.
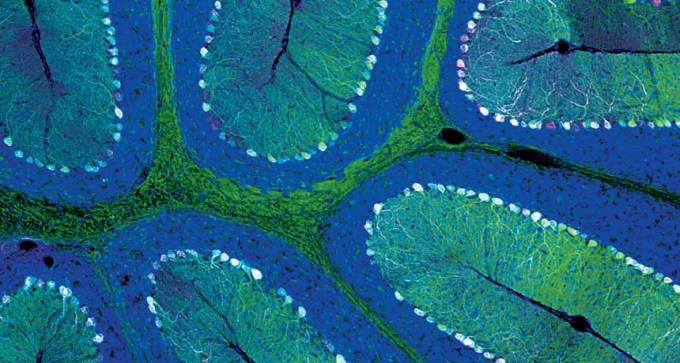
The virus AAV-PHP.B proves best at delivering genes to brain cells in mice. Similar viruses may eventually be used for gene therapy in humans.

Named for Johnny Cash, a new species of tarantula makes its home in the shadow of Folsom Prison.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

New all-in-one electronic device can detect and analyze your temperature and four chemicals in your sweat.

Babylonians took a geometric leap to track Jupiter’s movements long before European astronomers did.
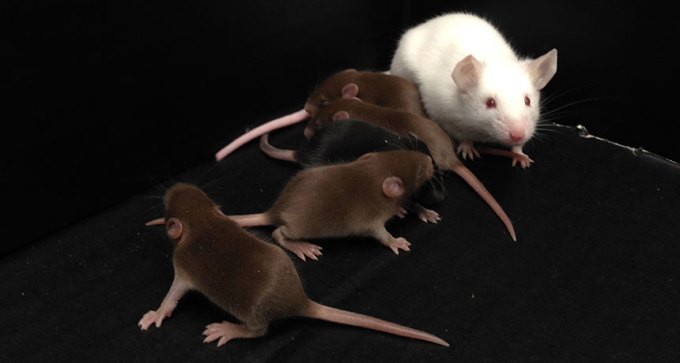
Researchers bypass the Y chromosome to make male mice.
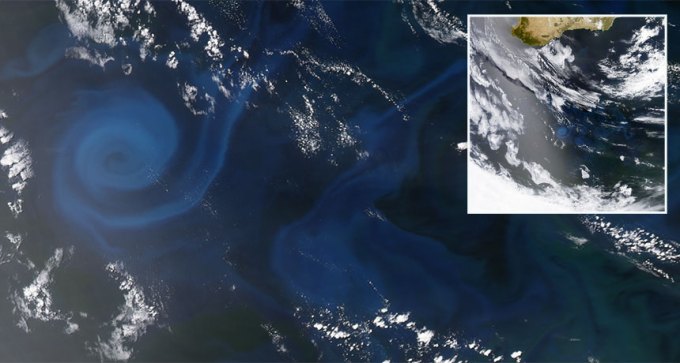
Phytoplankton populations in the Indian Ocean fell 30 percent over the last 16 years largely due to global warming, new research suggests.

Senescent cells promote aging, and removing them makes mice live longer, healthier lives.

The brain needs time to recover between head hits, a study in mice suggests.

The otherwise well-studied white-tailed deer turns out to carry the first malaria parasite discovered in any deer.

A preliminary report questions the anti-Alzheimer’s activity of a cancer-fighting drug.
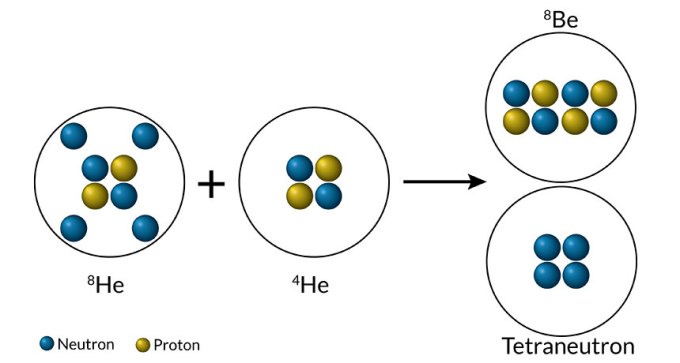
Strong evidence of a tetraneutron, an atomic nucleus with four neutrons but no protons, defies physicists’ theoretical expectations.

Arctic cities are a source of warming in the far north. Unlike midlatitude heat islands, poorly insulated buildings — not the sun — are a primary source.

Gravitational waves, tremors in the cosmic fabric of space and time predicted by Einstein a century ago, have finally been detected, opening a new avenue for exploring the universe.

Neandertal DNA may once have helped humans, but now may contribute to disease.

Smartphone app MyShake uses motion-sensing accelerometers to detect nearby quakes. The app could provide early warnings of incoming tremors, its creators say.

Animal studies and analyses of gene activity point to broad range of potential new health risks from vaping affecting everything from sperm to heart and immunity to mental health.

Deaf kids exposed to sign language from birth performed better on a task that required attention and impulse control.

Gas freezing onto dust grains around a binary star could be setting up a site where comets or even planets might someday form.
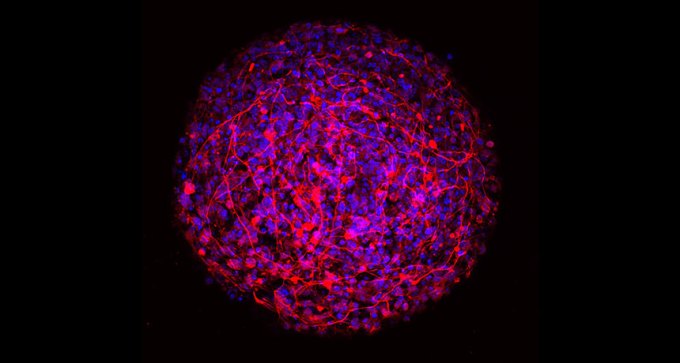
A reliable way to make standard-issue minibrains could help scientists study the human brain.

New analyses shed light on how ancient Egyptian “mummy paintings” were made.
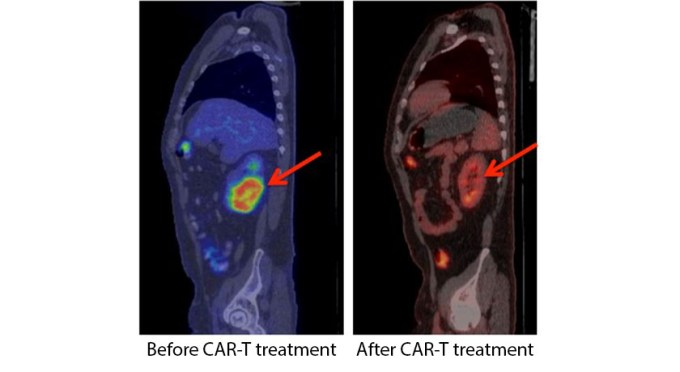
Immune therapy made more powerful with memory T cells.
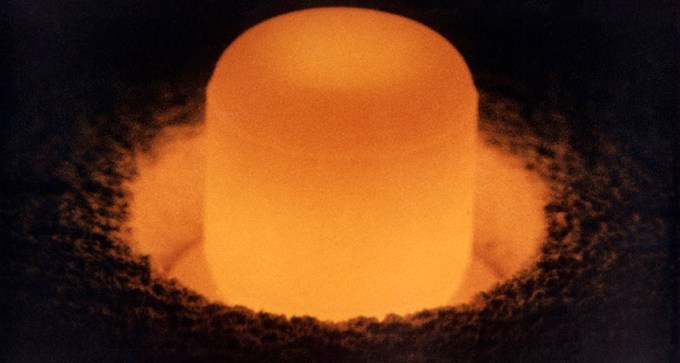
On the 75th anniversary of the discovery of plutonium, the radioactive element is still not a major source of fuel for nuclear power plants in the United States.

Diagnosis of a brain-wasting disease drove a married couple into science.

The Prodigy’s Cousin explores the baffling world of child prodigies and people with autism.

Morning people are more likely to have certain variations in their DNA, but less likely to have insomnia or sleep apnea.

For the first time, a computer has beat a professional human player in the strategy game Go.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.