‘Time Travel’ tours a fascinating fiction
James Gleick’s entertaining book Time Travel focuses more on fantasy than real science.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Shifting landmasses have repeatedly reshaped Earth’s surface. Researchers piecing together the past are now picturing a new supercontinent, due in 250 million years.

James Gleick’s entertaining book Time Travel focuses more on fantasy than real science.
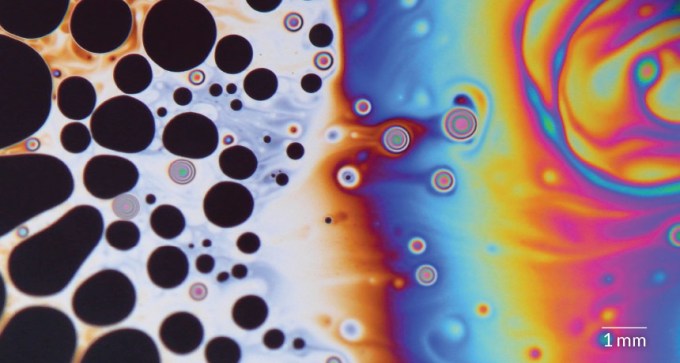
Merging dark spots are indicators that a bubble is about to burst.

Lava tubes inside the moon could remain structurally sound up to 5 kilometers across and offer prime real estate for lunar colonists.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

Next-generation batteries must hold more energy for longer periods at low cost. Several contenders may achieve some of these elusive goals.

Physicists used starlight to perform a cosmic Bell test.

The chemicals trigger drawstring-like structures that help close wounds.

Leaping robot can bounce from floor to wall, parkour-style, and, like a bush baby, uses a “super-crouch” to get extra oomph out of jumps.

New research confirms anecdotal reports that virtual reality headsets can cause motion sickness, and may affect women more than men.
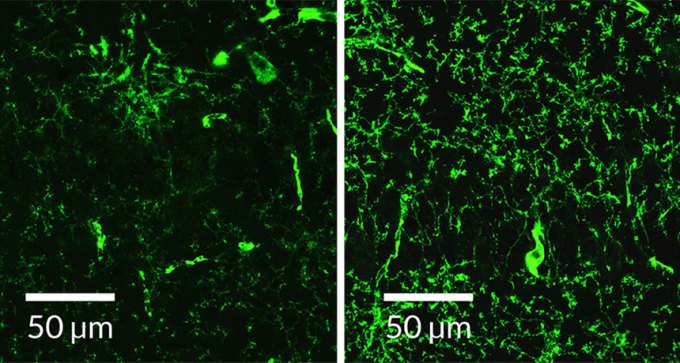
Flickers of light induce brain waves that wash amyloid-beta out of the brain, mouse study suggests.
Extra chromosome copies may protect against, not cause, cancer.

A new quasicrystal found inside a Russian meteorite is the first ever found in nature before being synthesized in the lab.
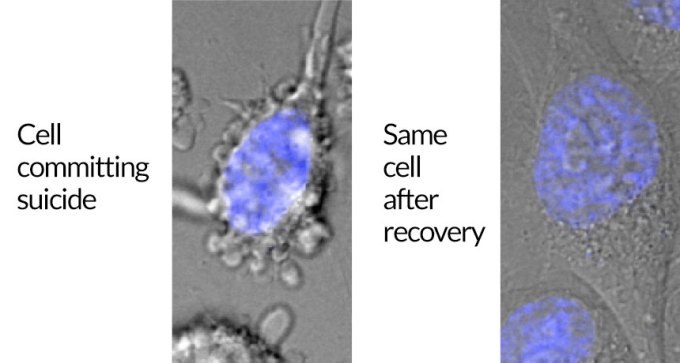
A newly discovered process can pull cells back from the brink of death.

The names of 227 stars have been formally recognized by the International Astronomical Union.

The decades-long melting of glaciers is categorical evidence of climate change, a new study affirms.

Pioneering microbes colonized the waters above the Chicxulub crater within hundreds of years following the impact, new research shows.
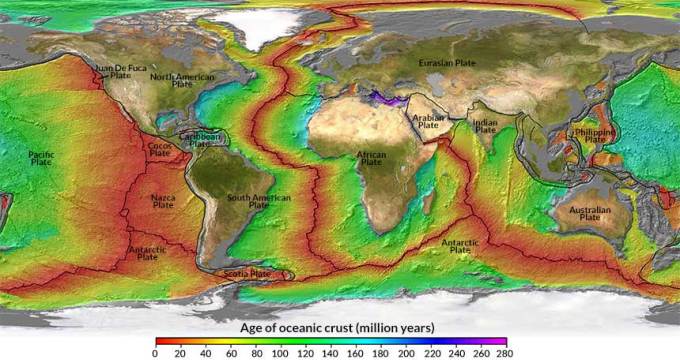
The thinning of newly formed oceanic crust suggests that Earth’s mantle is cooling much faster than previously thought.

About 6 percent of U.S. women infected with Zika virus have infants or fetuses with birth defects, according to preliminary CDC results. For women infected in the first trimester, the number is even higher: nearly 11 percent.

Water ice sits just beneath the surface and within some permanently shadowed craters of the dwarf planet Ceres.
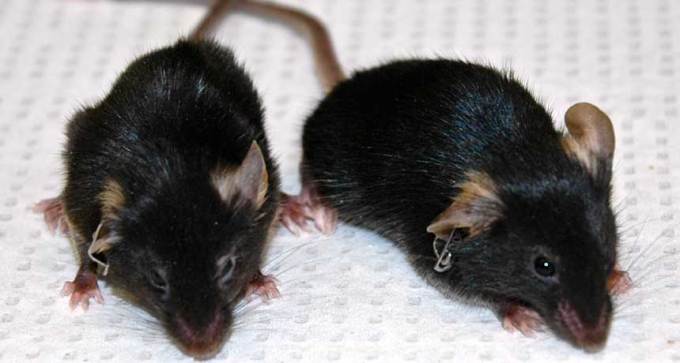
Proteins that reprogram adult cells to an embryonic-like state can rejuvenate prematurely aging mice.
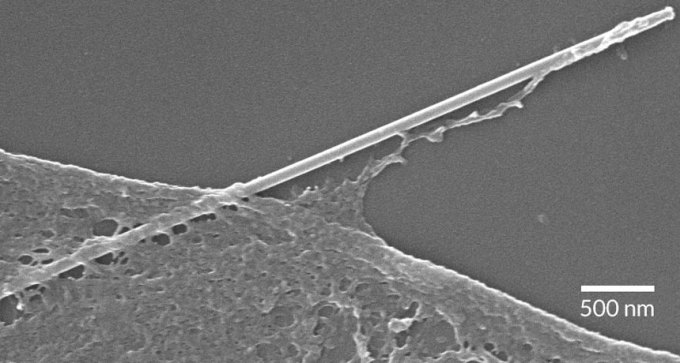
Human cells eat silicon nanowires in a process called phagocytosis. Nanowire-infused cells could be a step towards biological electronic devices.

Tracks discovered in Tanzania appear to have belonged to the tallest known Australopithecus afarensis individual, but stature estimates can be tricky.
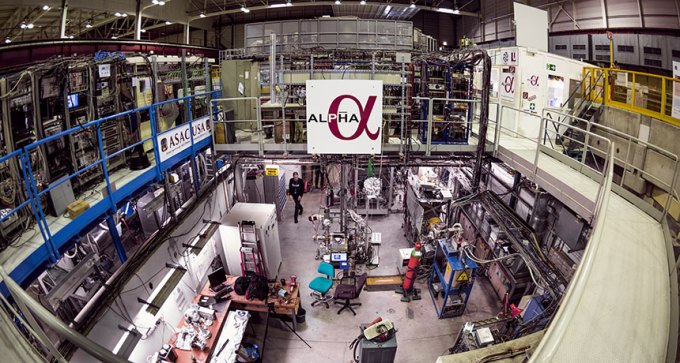
Antihydrogen atoms behave similarly to normal hydrogen atoms.

Rapid Arctic warming has increased emissions of carbon dioxide, but not methane, from northern Alaska tundra.

"Hidden Figures" tells the untold story of the "human computers" who were essential to the launch of the U.S. space program.
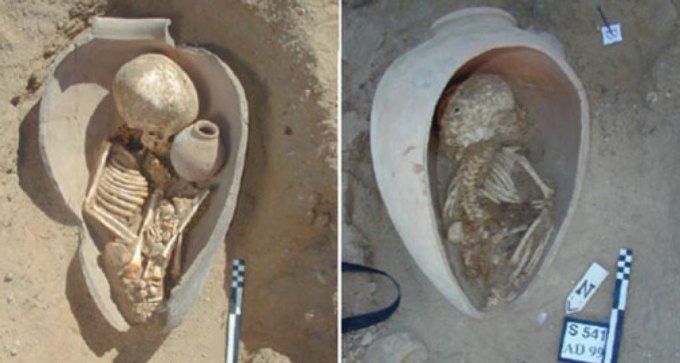
In ancient Egypt, using pots for burial containers was a symbolic choice, not a last resort, archaeologists say.

Fifty years ago, astronomers knew of 10 moons orbiting Saturn. Since then they’ve catalogued a diverse set of 62 satellites, with the help of the Cassini spacecraft.

"Furry Logic" explores how animals rely on the laws of physics in pursuit of food, sex and survival.

The Curiosity rover has found the first signs of boron on Mars, which could hint at past habitable groundwater.
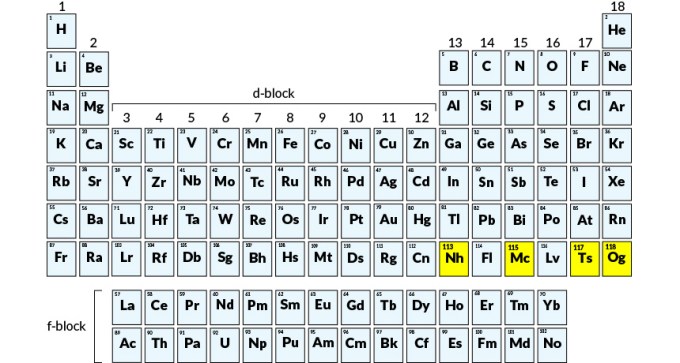
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry has approved the proposed names for the four elements added to the periodic table in December 2015.
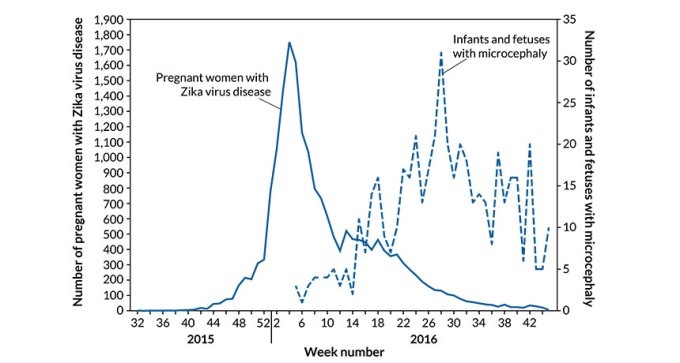
More than 400 cases of microcephaly have been reported in Colombia this year, months after Zika virus infections peaked in the country.

Cell biologists are learning more about how the Zika virus disrupts brain cells to cause microcephaly.

Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.