A new book explores the link between film giant Kodak and the atomic bomb
In Tales of Militant Chemistry, Alice Lovejoy traces how film giants Kodak and Agfa helped produce weapons of war during the 20th century.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Diagnoses for several cancers before age 50 have been increasing rapidly since the 1990s. Scientists don’t know why, but they have a few suspects.

In Tales of Militant Chemistry, Alice Lovejoy traces how film giants Kodak and Agfa helped produce weapons of war during the 20th century.

Researchers reconstructed a roughly 2,000-year-old woman’s tattoos, from prowling tigers to a fantastical griffinlike creature.

Asteroid impacts, microbes, mining: These are a few tactics engineers might one day use to create an Earthlike atmosphere on Mars.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

The Nobel Prize might be the most famous science prize but it celebrates just a narrow slice of science and very few scientists.

A slew of new research attempts to zero in on what happens as our brains get older — and what can bring about those changes early.

Some people’s biology may set them up to birth babies of a certain sex, explaining why a family with multiple children may have all girls or all boys.

Research based on game theory suggests if we program AI agents with a sense of guilt, they could behave more cooperatively, much like humans do.
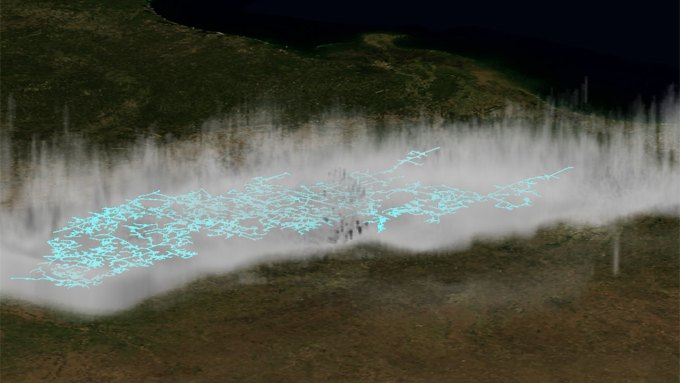
A reanalysis of satellite data shows that a 2017 Texas-to-Missouri lightning megaflash stretched 829 kilometers and lasted 7.39 seconds.
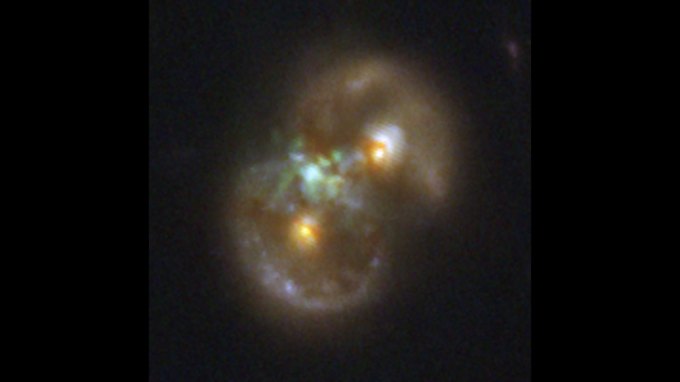
An infinity symbol–shaped galaxy hosts an active supermassive black hole. The growing giant may have come from the aftermath of a galactic smashup.

Quantum computers in space could be useful for communications networks or for testing fundamental physics.

The enamel in fossilized teeth reveals some dinosaurs preferred to eat particular parts of plants.

An analysis of the Res Gestae Divi Augusti using AI reveals its legal tone and imperial messaging, offering new insights missed by historians.

Knowing potatoes’ origin story could help future-proof the crucial crop against climate threats.
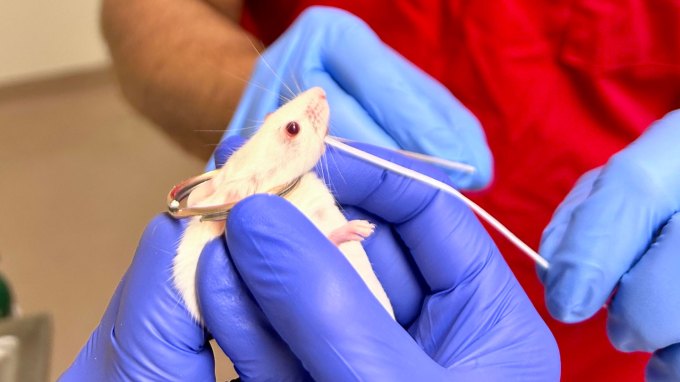
Flu viruses often enter the body through mucous tissue in the nose. Researchers are developing new ways to protect such areas.
The superclouds probably produce star-forming clouds of gas, since most nearby stellar nurseries are located within the giants.

Revealed by advanced imaging, the long-sought "Betelbuddy" is much smaller and fainter than Betelgeuse and orbits within the supergiant’s atmosphere.

An analysis of 57 studies shows that people who walked a certain number of steps were less likely to die from any cause compared with those who walked less.

Seeing sick-looking faces in virtual reality triggers brain circuit changes related to threat detection and boosts activity of certain immune cells.

A bacterium called Vibrio pectenicida may be melting sea stars along North America’s Pacific coast.

Sun-powered fliers could use photophoretic forces to hover in the mesosphere, gathering data from a region off limits to planes and balloons.
Golden apple snails can regrow full, functional eyes. Studying their genes may reveal how to repair human eye injuries.

After a sprint, the temperature of the beetle Onymacris plana drops. Efficient running, a body built for cooling and a little bit of lift all help.

Anxious dogs might react nervously to some television sounds, a survey of dog owners reports, while hyper ones might try to play chase.
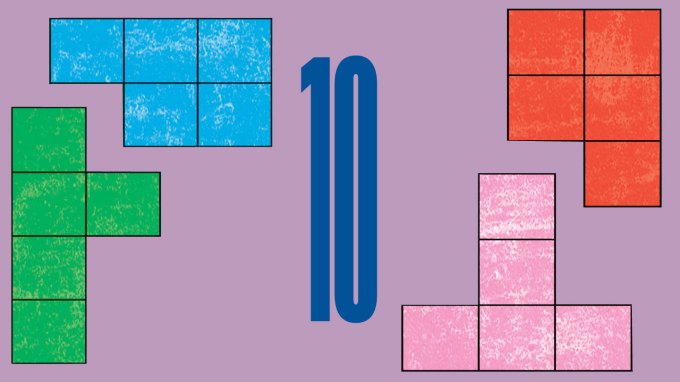
Solve the math puzzle from our October 2025 issue, in which four princesses divide up lands to keep peace.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.